Understanding Hand Fractures: Types, Symptoms, and Treatment Options with Visual Guides
The hand is critical for a wide array of daily tasks, ranging from gross motor movements involved in eating or writing to fine motor movements in working or sports. A hand fracture will affect these functionalities and disrupt daily life through pain and restricted mobility. Proper understanding of hand fractures enables their recognition and prompt and respective treatment. Exemplary tools like hand fracture pictures aid in identifying the fracture's type and severity. They aid understanding and informed decision-making regarding treatment. This blog post aims to educate readers about the types of a hand fracture, their symptoms, and treatment options along with hand fracture images for an easier understanding.
Section 1: What is a Hand Fracture?
A hand fracture is a break in one of the 27 bones of the hand, such as the finger bones, metacarpals, or wrist. A hand fracture occurs when a bone breaks as a result of some external force, commonly due to trauma: a direct blow, exertion of excessive force, or twisting trauma.
The most common causes of hand fractures
These fractures are due to accidents, falls, or any high-impact activities, such as sports. Tripping or banging the hand against a hard surface are common everyday activities that cause hand fractures.
Importance of Early Recognition
The purpose of fracture identification, especially when they occur in the hand, is to prevent future complications. Hand fracture images, including X-rays, facilitate diagnosis and indicate when it is appropriate and safe enough to commence said treatment, thus allowing the fracture to heal properly and restore full motion function.
Section 2: Types of Hand Fractures with Visual Guides
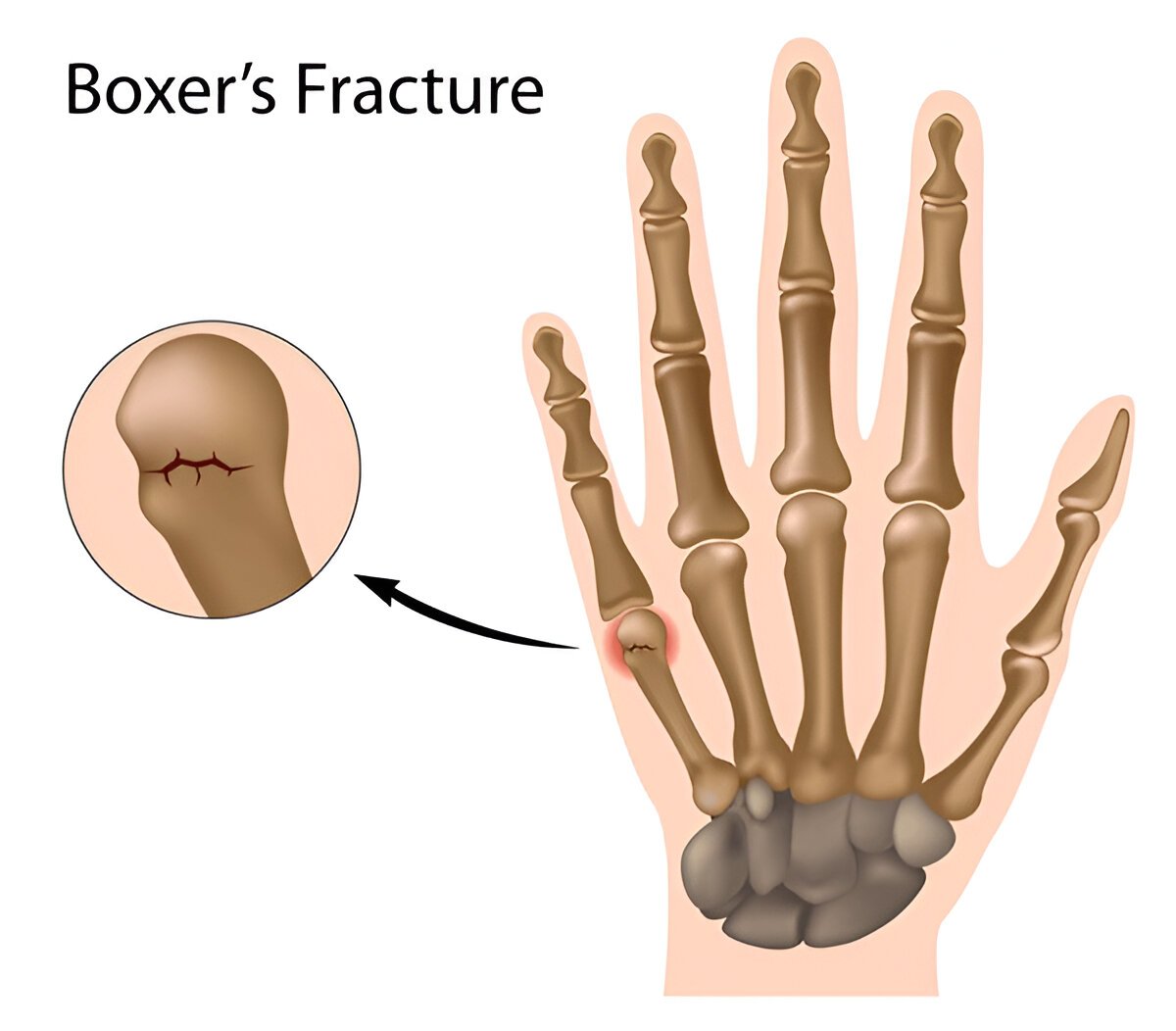
1. Boxer's Fracture
Boxer's fracture is one that crosses through the metacarpal bones, frequently the fourth or fifth metacarpal. Most common cause is impact of punching a harder object. Symptoms include swelling, bruising, and pain. X-rays can show the region of concern for an increased diagnosis.
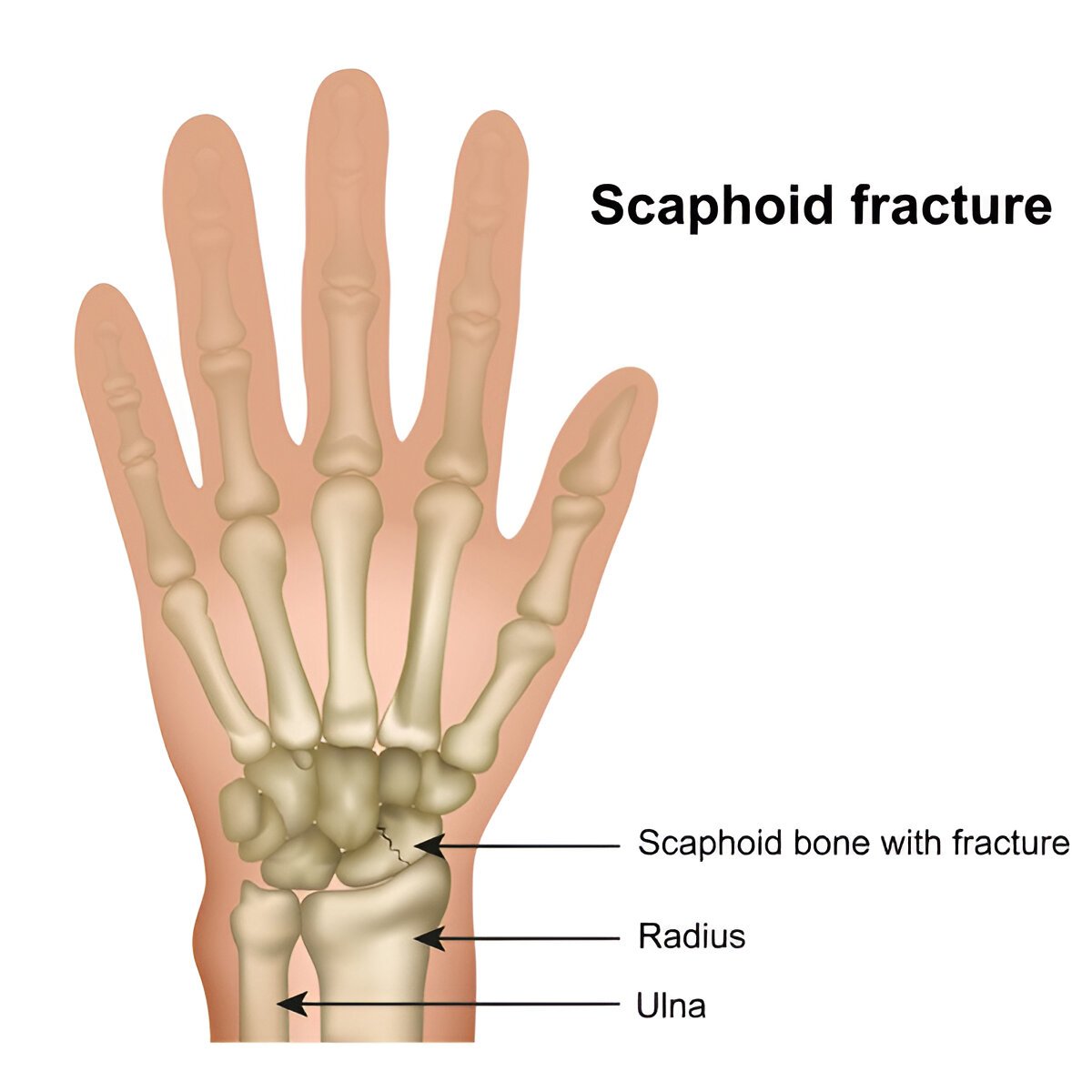
2. Scaphoid Fracture
The fracture, which involves the scaphoid bone, occurs due to falling on an outstretched hand. Pain and tenderness in and around the thumb and wrist are the chief complaints. X-ray scans provide clear visuals of the scaphoid fracture for accurate treatment.
3. Phalangeal Fracture (Finger Fracture)
Phalangeal fractures involve one or more breaks in the finger bones caused by sports injuries or crushing accidents. Symptoms include swelling, pain in the finger, and an inability to move the finger. X-rays can pin down the broken finger for proper care.
.jpg)
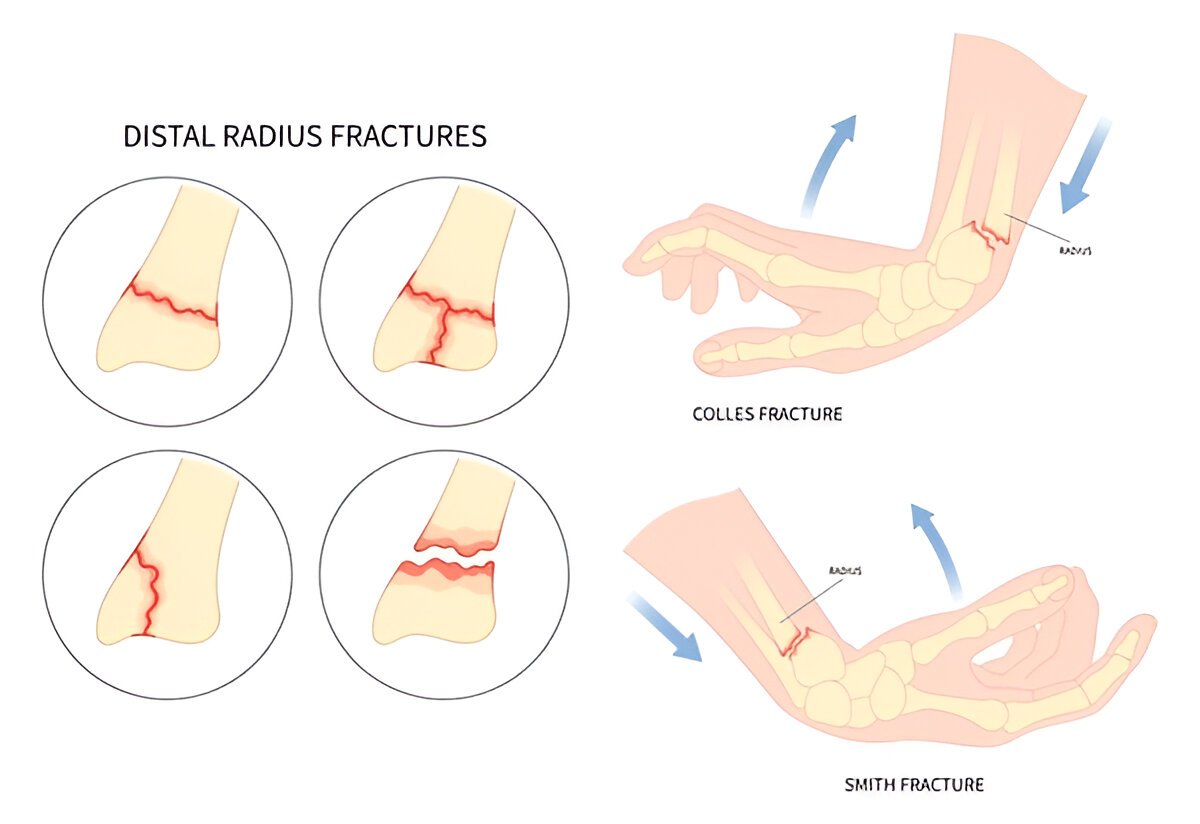
4. Distal Radius Fracture
A distal radius fracture occurs near the wrist joint involving the radius bone and is usually caused by a fall on an outstretched arm. Symptoms include wrist pain, swelling, while possible deformity may take place. The X-ray image helps to identify the type and the severity of that fracture.
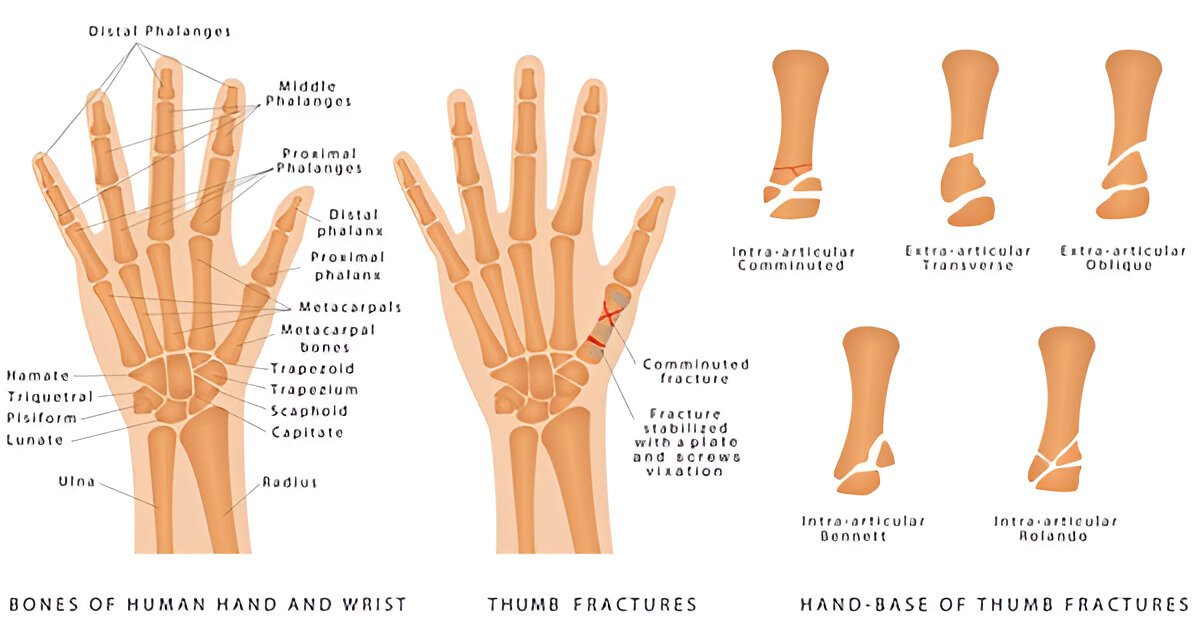
5. Thumb Fracture
Thumb fractures are breaks in either the proximal or distal phalanx of the thumb. The injuries are generally the result of sports accidents or falls. Symptoms are pain, swelling, bruising, and trouble grasping objects. This X-ray helps visualize the broken thumb for diagnosis.
Section 3: Symptoms of Hand Fractures
Hand fractures exhibit varying symptomatic degrees upon production. Swelling and pain around the injured area are almost invariably present. Bruising and discoloration may appear as the injury progresses. A clear indication of a fracture is the deformity or misalignment of the fingers or hand, in which case the bones may appear to be out of place. Due to pain or structural damage, you may find it difficult to move, or are unable to move, the affected fingers or hand. Images, like X-rays, of the hand fracture are very helpful in determining the site and look for the fracture thereby creating formulations for treatment by the doctor for faster and complete recovery.
Section 4: Diagnosing Hand Fractures
Prompt medical evaluation is essential when a hand fracture is suspected. That means early diagnosis is critical because it ensures proper treatment, prevents complications, and minimizes long-term effects such as stiffness or deformity. Ignoring symptoms may cause further injurious effects.
Diagnostic Procedures
Diagnosis begins with a thorough physical examination by an orthopedic doctor who evaluates the hand for pain, swelling, and mobility. They may also look for signs of deformity or tenderness to locate the fracture.
Role of X-Ray Images
X-ray scans are critical for confirming the type and severity of a hand fracture. The images provide vivid visuals that help the doctor determine the most desirable option of treatment tailored to the specifics of the injury.
Section 5: Treatment Options for Hand Fractures
Non-Surgical Treatments
Most hand fractures can heal without surgery. They are stabilized through splinting or casting, allowing them to heal naturally. Afterward, physical therapy will usually follow to regain strength, mobility, and function. Pain relief medications will also be prescribed to relieve discomfort during recovery.
Surgical Treatments
Surgery is needed in facial conditions where there are broken bones with severe misalignment, where the bones do not heal properly, or where complicated fractures occur. Common surgical procedures include internal fixation with screws or plates and pinning to hold the broken pieces. These methods ensure that functionality and alignment of the hand are restored.
Post-Surgery Care
Adequate care following surgery is essential. Follow your doctor's instructions, attend the therapy sessions, and rest properly for easy recovery.
Section 6: Recovery and Rehabilitation for Hand Fractures
The duration for which hand injuries take to heal depends on the severity and type of injury. Simple fractures can heal in about 4-6 weeks while complex fractures or those treating it surgically may take several months before knitting properly. Do follow the treatment plan before you achieve a complete recovery.
Physical therapy is critical for greater strength, movement, and manual dexterity in the hand. Exercise in the health unit is performed under the supervision of a trainer and is aimed at rebuilding muscle power, increasing range of motions, and protecting against rigidity or shrunken joints.
The following simple preventive methods can be employed so as not to end up with yet another fracture: wearing protective gear while engaging in sports; using ergonomic tools; sticking with safe lifting techniques. The other thing is to know when to stop to keep the hand protected from injury.
Section 7: When to Seek Orthopedic Care
If after a hand injury, certain signs crop up, it is important to seek the immediate help of an orthopedic surgeon. The main problem with persistent pain that does not seem to get better with rest or over-the-counter treatments is that it may be an able indicator of a more serious problem. Swelling that does not subside within a reasonable time, or at the very least stops getting worse, is greatly worth your time and attention. Other issues are with odd deformities being visible from the sides such as misalignment of bones and unusual shapes that are seen to occur along the outer 4th or 5th WBCs. Or if the patient is simply having trouble moving the hand or keeping a firm grip on an object or keeping with daily activities. If so, go straight to seek medical assistance from the orthopedic surgeon in time; it will ensure the diagnostic and therapeutic range is wide open and in place.
Conclusion
The prompt and early identification of a hand fracture is critical to effective management of an injury that might lead to complications like stiffness or deformity. Early diagnosis permits timely care and offers the best chances for rehabilitation. Knowing even an ounce of such knowledge can mean saving lives, let alone rehabilitating a hand fracture. The best orthopedic doctor in Jaipur recommends proceeding with an x-ray photograph to understand the levels of fracture and what the type of treatment would be proceeded with. Don't wait! Book an appointment to protect your hand health and get one step closer to recovery.
Read MoreFaq’s
1. What are the most common types of hand fractures?
Hand fractures include the Boxer's fractures (the 4th/5th metacarpals), the scaphoid fractures (the carpal bones), phalangeal fractures (the digits), distal radius fractures (near the wrist), and thumb fractures. Most of the time, falls, sports injuries, or accidents are the causes of these types of injuries.
2. How can I identify a hand fracture?
Symptoms include pain, swelling, bruising, deformity, and difficulty moving the hand or fingers. Tenderness at the injury site is also common, and deformity may be visible in severe cases.
3. What treatment options are available for hand fractures?
Surgical intervention may be an option for fractures if the injury displacement necessitates realignment. An orthopedic specialist will decide the treatment options based on the severity of the fracture. Since hands contain several bones and are often used, they may take even longer than a few months to properly heal.
4. How long does it take to recover from a hand fracture?
Simple fractures heal in 4-6 weeks, while complex or surgical cases may take months. Physical therapy often follows to restore strength and mobility.
5. When should I see an orthopedic surgeon for a hand fracture?
Seek an orthopedic surgeon if there’s persistent pain, swelling, deformity, or difficulty moving the hand. Worsening symptoms like increased numbness or severe swelling also require immediate attention.